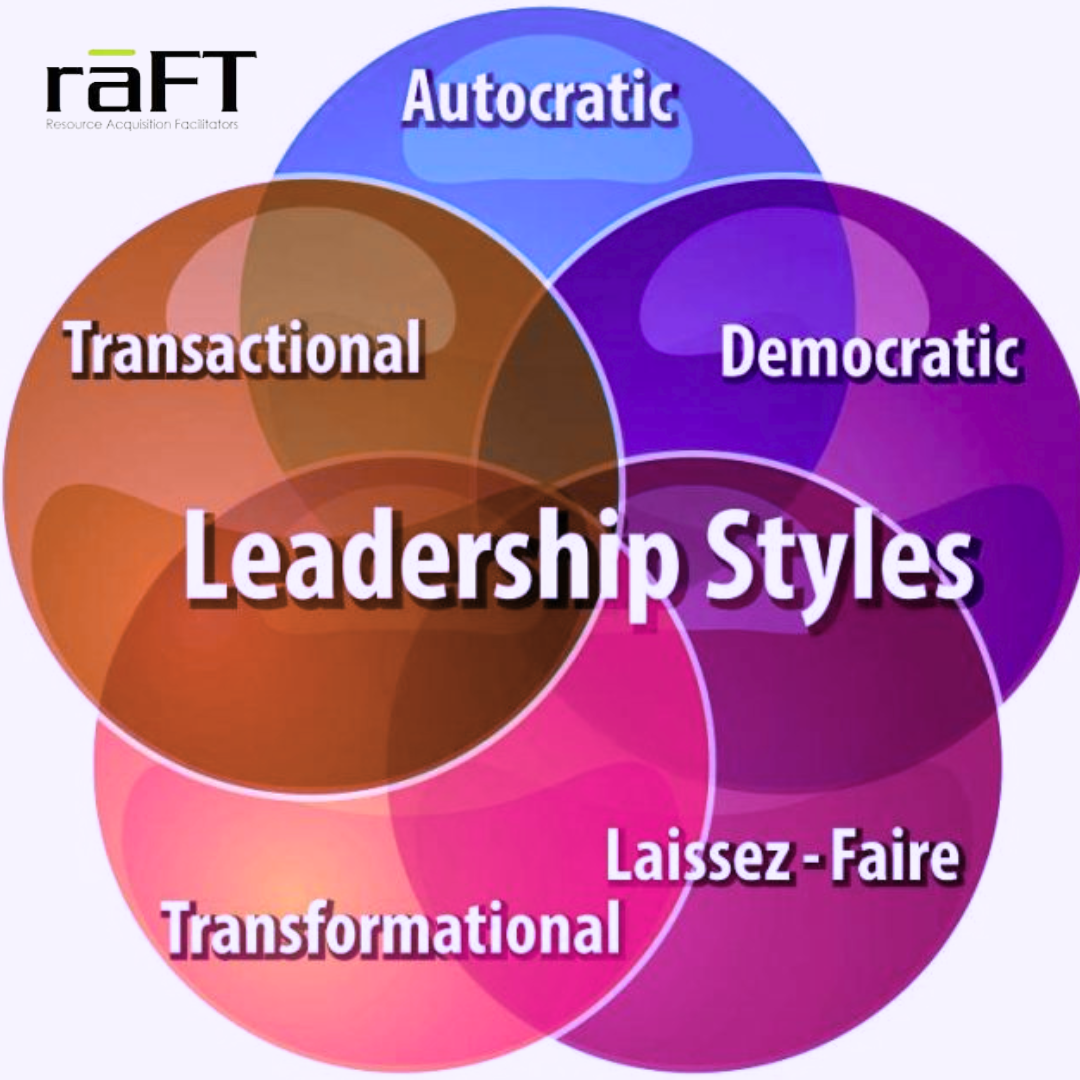
Leadership styles refer to the approaches, behaviors, and attitudes that leaders employ to guide, motivate, and manage their teams or organizations. There are various leadership styles, each with its own characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. Some common leadership styles include:
- Autocratic Leadership: In this style, the leader makes decisions without consulting team members. They exercise full authority and control over the team, expecting obedience and compliance. While it can lead to quick decision-making, it may also stifle creativity and motivation among team members.
- Democratic Leadership: Also known as participative leadership, this style involves the leader encouraging input and participation from team members in decision-making processes. It fosters collaboration, creativity, and a sense of ownership among team members, but it can sometimes lead to slower decision-making.
- Laissez-Faire Leadership: This hands-off approach involves the leader delegating tasks and responsibilities to team members with minimal guidance or supervision. It empowers team members to take ownership of their work but can lead to a lack of direction and accountability if not managed effectively.
- Transformational Leadership: Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their teams by setting a compelling vision and empowering them to achieve it. They focus on developing and mentoring their team members, fostering a culture of innovation and growth.
- Transactional Leadership: Transactional leaders focus on clarifying roles and responsibilities and establishing clear rewards and consequences for performance. They emphasize structure, efficiency, and meeting predetermined goals and objectives.
- Servant Leadership: Servant leaders prioritize the needs and development of their team members above their own. They focus on serving others, fostering trust, and empowering their team to reach their full potential.
- Charismatic Leadership: Charismatic leaders possess strong charisma, charm, and persuasion skills, which they use to inspire and influence their followers. They often have a compelling vision and the ability to rally people around it.
- Bureaucratic Leadership: Bureaucratic leaders adhere strictly to rules, procedures, and protocols. They prioritize stability and predictability but may struggle to adapt to change or foster innovation.
- Coaching Leadership: Coaching leaders focus on developing the skills and capabilities of their team members through guidance, feedback, and support. They prioritize individual growth and development to enhance overall team performance.
- Adaptive Leadership: Adaptive leaders are flexible and able to adjust their approach depending on the situation and the needs of their team. They prioritize learning, agility, and resilience in navigating complex and dynamic environments.
Different situations may call for different leadership styles, and effective leaders often exhibit a blend of styles depending on the context and the needs of their team or organization.